Measuring Moisture Content In Concrete Walls

The test is performed by sealing an insulated box to the concrete and measur ing the relative humidity inside the box with a calibrated capacitance based humidi ty gauge.
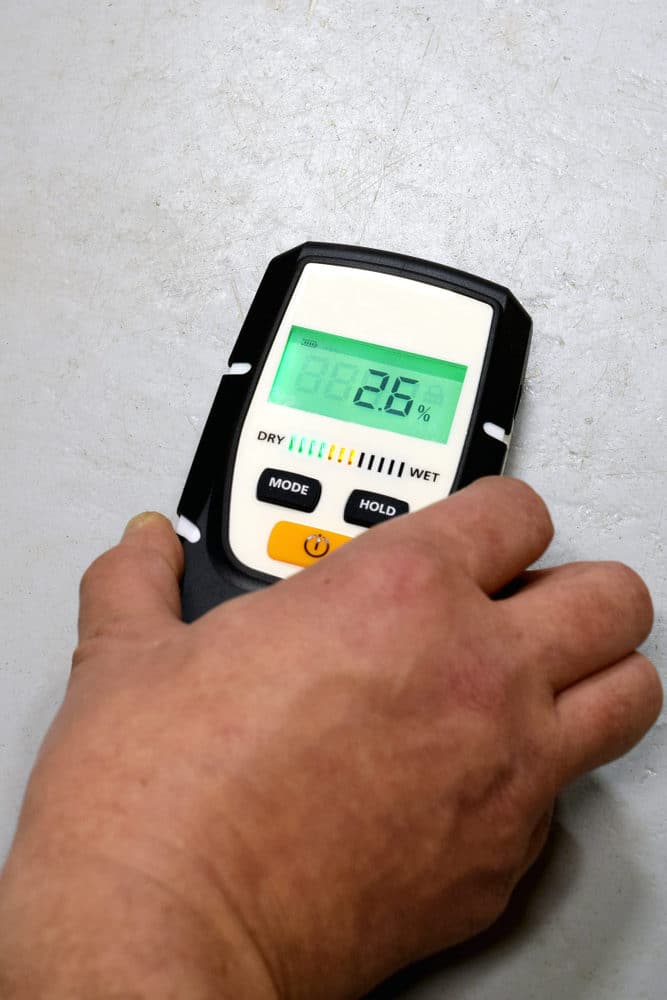
Measuring moisture content in concrete walls. This is a relative scale. Structural and safety hazards such as mold rot and decay are all potential consequences of elevated moisture levels in these materials. The ability to detect moisture accurately in both wood and drywall makes this device particularly suited for building inspection work. Check for surface discoloration such as yellowing material.
How concrete hardens and dries concrete is manufactured by mixing cement aggregates such as sand and gravel and water. Additionally some meters also offer a third scale for readings of gypsum. Often more than one method is used to get an accurate reading of actual moisture content. The bd 2100 s drywall moisture meter readings are accurate in gypsum to moisture content percentages as low as 0 2 and as high as 50.
These scale readings can range from 0 2 to 50 moisture content. Under this method you ll use a thermo hygrometer with in situ probes along with a series of prepared holes to get readings of relative humidity deep in the concrete slab. When testing the moisture content in non wood materials such as concrete a relative scale of 0 to 100 is often used where 0 is bone dry and 100 is saturated. In the wood scale the meter can detect moisture accurately over a range of 6 mc to 40 mc.
Since we know that moisture within a slab varies by depth any moisture test that only measures moisture at the surface can t give you consistently reliable usable results. To test for moisture inside the walls start with manual tests and proceed to moisture meters. There are three standard methods for measuring concrete moisture. Moisture meters include visual led indicators related to the percent reading on the scale for dry moderate and saturated or wet readings.
You see the cacl test and most other concrete moisture testing procedures employ methods such as the plastic sheet application only measure moisture escaping from the surface of the concrete slab. If the concrete is at 5 percent moisture content it will neither absorb nor desorb moisture if the air above it is 70 f 21 c and 75 percent rh. A separate reference scale setting can be used for getting qualitative readings of moisture in other wall materials like plaster. Therefore measuring rh levels at 40 depth of the slab 20 depth if drying on two sides is more representative of the overall humidity conditions of the concrete.
According to astm f2170 when drying concrete slabs have lower moisture levels near the surface and higher levels towards the bottom of the slab. Look at the wall surface carefully.