Melting Point Of Ethyl Vinyl Acetate

At 50 c the solubility of vinyl acetate in water is 0 1 wt more than at 20 c but the solubility of water in vinyl acetate doubles to about 2 wt.
Melting point of ethyl vinyl acetate. As the va content increases crystallinity decreases until at 50 the eva is. Ethylene vinyl acetate is a type of plastic a polymer with a wide variety of uses both residential and industrial. 1 201 767 0743. At low to moderate doses it produces irritation at the point of contact.
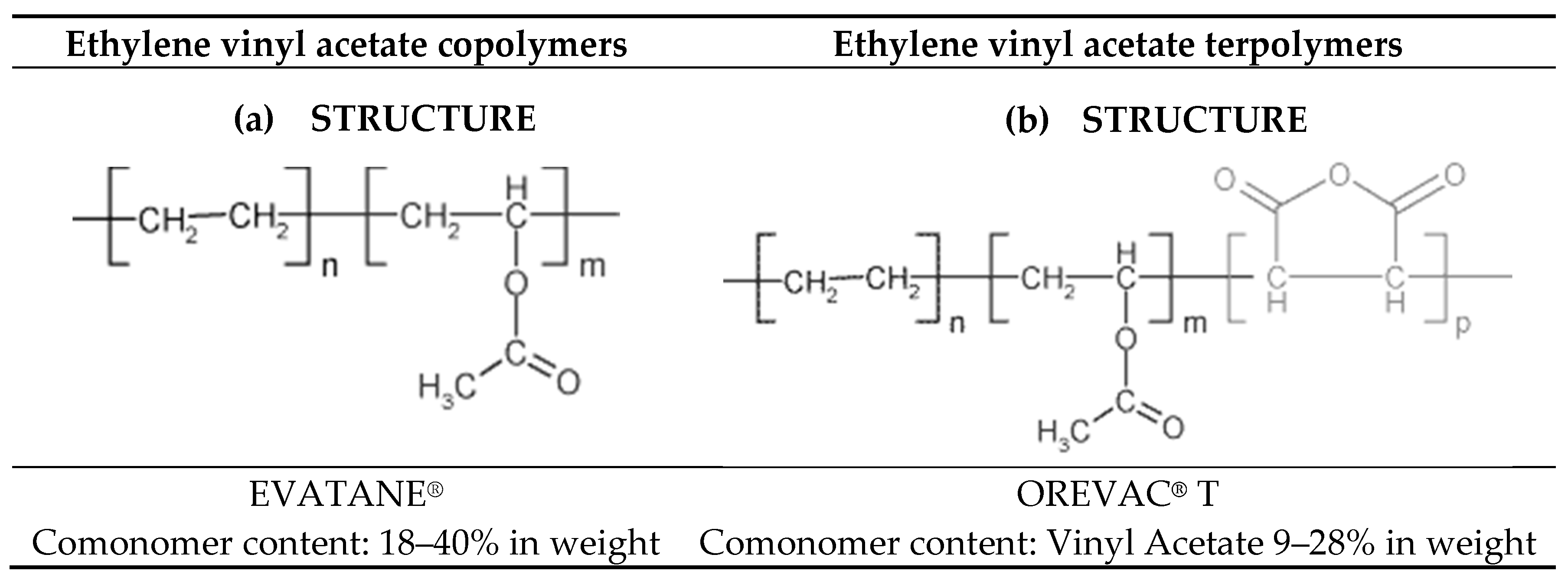
Ethylene vinyl acetate eva is a random copolymer of ethylene and varying amounts of vinyl acetate va. Emblem in packaging technology 2012. Ethylene vinyl acetate eva also known as poly ethylene vinyl acetate peva is the copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate the weight percent of vinyl acetate usually varies from 10 to 40 with the remainder being ethylene. Melt index 57 g 10 min 190 c 2 16kg contains 200 800 ppm bht as inhibitor 437247.
Poly ethylene co vinyl acetate vinyl acetate 40 wt. Articles of ethyl acetate are included as well. The va comonomer interferes with chain packing reducing crystallinity and thus lowering t m and improving transparency when compared with ldpe. 1 201 767 0414 fax.
Chemsrc provides ethyl acetate cas 141 78 6 msds density melting point boiling point structure formula molecular weight etc. At 20 c a saturated solution of vinyl acetate in water contains 2 0 2 4 wt vinyl acetate whereas a saturated solution of water in vinyl acetate contains 0 9 1 0 wt water. Robles in encyclopedia of toxicology third edition 2014. The food and drug administration fda has stated that ethylene vinyl acetate is safe when used in food production packaging or transportation and it s not an especially dangerous material.
Melting point density additive chemical composition melt index hardness. There are three different types of eva copolymer which differ in the vinyl acetate va content and the way the materials are used. 1 dewolf rd suite 210 old tappan nj 07675 usa tel. Vinyl acetate is the acetate ester of vinyl alcohol.
Vinyl acetate is moderately toxic when administered through ingestion inhalation and peritoneal injection. The major industrial route involves the reaction of ethylene and acetic acid with oxygen in the presence of a palladium catalyst. Following ingestion or inhalation vinyl acetate is rapidly metabolized by carboxylesterases to form acetaldehyde and acetic acid. Since vinyl alcohol is highly unstable with respect to acetaldehyde the preparation of vinyl acetate is more complex than the synthesis of other acetate esters.


























.jpg)